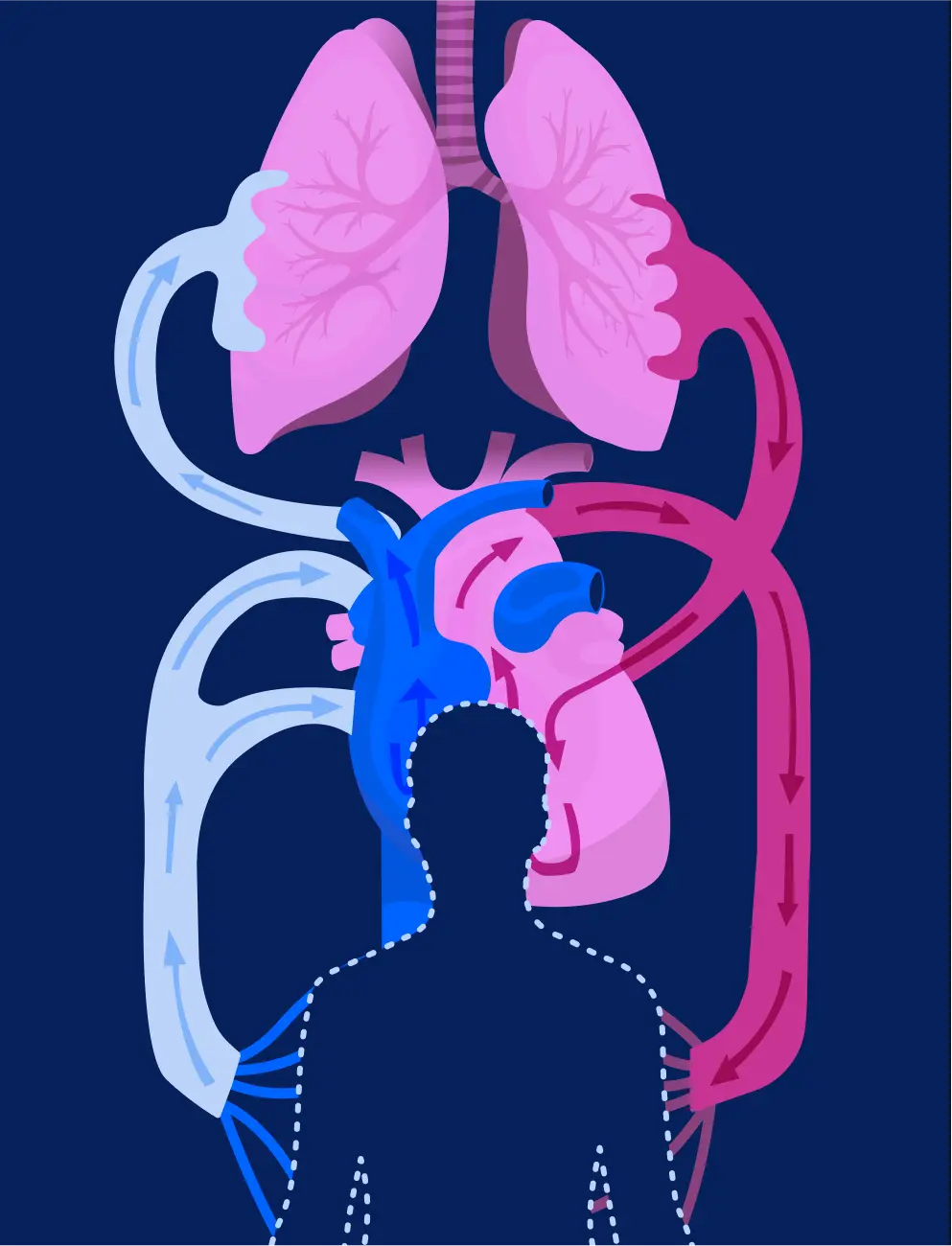
Your heart and your lungs are two of the most vital organs in your body. In addition to sharing a chest cavity, the functions of the heart and the lungs are closely intertwined.
How it Works
With each beat, your heart sends blood throughout the body. The pulmonary loop, or the right side of the heart, is tasked with collecting the oxygen-poor blood and moving it to the lungs for cleaning and reoxygenating. Once reoxygenated, the systemic loop, or the left side of the heart, pumps the high-oxygen blood to the rest of your organs; like the kidneys, liver and brain. Once all the oxygen in your blood has been consumed, the process repeats. With each inhale, your lungs fill with fresh oxygen and each exhale releases carbon dioxide – ensuring the blood your heart pumps is meeting the needs of your body.
Though it seems complex, the two systems work together so seamlessly that it takes about 16 seconds for blood to travel through the body, allowing about five quarts of blood to circulate per minute. When everything is running smoothly, you are considered in good cardiopulmonary health.
Common ‘Relationship’ Problems
The dependency of these two systems means that, when a problem occurs, it can cause bigger problems. “Unfortunately, the cardiovascular (heart) and respiratory (lungs) systems are so connected that, if either one has a problem, it may also cause the other to fail,” said Dr. Albert Rizzo, the American Lung Association’s Chief Medical Officer.
Heart failure prevents the heart from pumping enough oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. However, depending on the side that heart fails, it can also cause shortness of breath and strain on the lungs.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) causes the airways in your lungs to become inflamed and thicken, making it harder for oxygen to travel in and out of your lungs. This in turn can cause a rise in blood pressure, known as pulmonary hypertension, which puts stress on the right-side of the heart and can cause it to fail.
There are many other chronic diseases that can cause these two essential organs to fail. Common symptoms that may signal a cardiopulmonary problem include chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, swollen legs, dizziness and fatigue.
Keeping Your Heart and Lungs Happy
Your heart and lung health are so essential to your overall wellness, and lifestyle changes can make a big difference in keeping them healthy.
Quit Smoking: Smoking narrows lung passages and makes it more difficult to breathe, therefore delivering less oxygen to your lungs and bloodstream. Over time, smoking can permanently destroy lung tissue and cause chronic diseases like COPD and lung cancer. But as soon as you quit, your body begins to repair itself. Read a list of benefits you will experience.
Exercise Regularly: When you are physically active, your heart and lungs work harder to get extra oxygen to your muscles. So, not only are you making your muscles stronger, but every time you do aerobic or strength training exercises, you are strengthening your lungs and heart. As your physical fitness improves, your body becomes more efficient at getting oxygen into the bloodstream and transporting it.
Eat Healthy: No single food will supply all the nutrients you need so a healthy diet has a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, protein and healthy fats. The right mix of nutrients in your diet can not only prevent problems but can help strengthen your lungs and heart. For instance, foods that are high in omega-3 fatty acids decrease inflammation in the arteries surrounding your heart, helping it work better. Conversely, foods high in salt can increase your blood pressure and strain your heart and lungs. Nutrition is particularly important to monitor for those with a chronic condition like COPD.
Reduce Stress: Hormones released during stress can have a negative impact on your heart and lungs. This link is shown by symptoms like an increased heartbeat and rapid, shallow breathing. Practicing relaxation techniques and mindful breathing is just one way to train your body to better respond to stressful situations. Get some more helpful tips.
Get Enough Sleep: Sleep is an important part of maintaining overall health which is why most experts suggest 7-9 hours are needed a night. Lack of sleep can impair your body’s functions overall and leave you feeling stressed.
Blog last updated: February 2, 2026